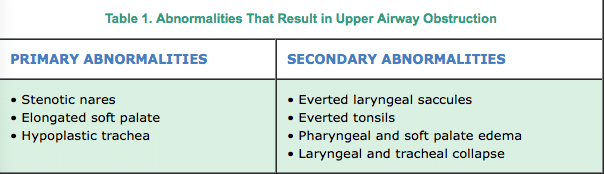
Brachycephalic airway syndrome (BAS), also sometimes referred to as Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome (or BOAS) refers to a group of primary and secondary abnormalities (Table 1) that result in upper airway obstruction. Primary abnormalities cause an increase in negative pressure within the upper airways that can eventually lead to secondary abnormalities. We absolutely do NOT want the Staffordshire Bull Terrier to continue down the path of the BAS affected breeds such as French Bulldog or Pug. We are NOT a brachycephalic breed and we don’t wish to be in that category for many reasons. Aside from stenotic nares, BAS can also include Elongated Soft Palate, Everted Laryngeal Saccules, Hypoplastic Trachea and Everted Palatine Tonsils.
Any tissue that obstructs the airway lumen is a source of resistance. According to the laws of physics, resistance in a single tube is inversely related to the radius raised to the fourth power. For example, if an airway is 50% obstructed, it is 16× harder to breathe, and if the diameter of any component of the upper respiratory tract is increased by 50%, resistance encountered on inspiration is decreased 16×.
Typical clinical signs of BAS are listed in Table 2; dogs with these signs benefit from early surgical correction of existing primary abnormalities before secondary changes occur. For example, in puppies with stenotic nares it is recommended to perform rhinoplasty at 3 to 4 months of age, and at the same time perform a preliminary evaluation of the soft palate. Addressing these primary abnormalities at an early age may help avoid progression to secondary changes such as everted laryngeal saccules or laryngeal collapse. There are veterinarians across the country specializing in correcting these abnormalities.
It is possible to have your Stafford scoped so that you are aware of any BAS related issue which could be present. If you plan to breed your Stafford, I would highly recommend doing this anyway. You cannot see all issues visually and for reproductive responsibilities, this should be conducted. I had my stud dog scoped by an experience veterinarian. Not because he has stenotic or pinched nares but because he is very active in a hot, humid environment and I needed to know he was not going to have breathing issues while working out. I also feel that to be a responsible breeder, including stud owner, this was the prudent thing to have done, along with all other health testing available to us. He has zero issues by the way, but personally I would like to see his nares more wide open and a bit more leather on his nose. It would be quite helpful if these scopes could be given an OFA certificate/number so it can be posted and made available in the OFA Database, but you can make note of this in the SBT Pedigree Database. You can also include this information in any stud or sales agreement.

If you look at the profile of a Staffords muzzle and nose you will see slight differences in the shape and positioning of the nose leather itself in affected and not affected animals. Usually, not always, a Stafford with wide open nares will have a more rounded and forward sitting profile to the nose leather. A Stafford whose nares are pinched almost seem to be missing a little bit of nose leather at the upper tip from profile, therefore the profile appears ever so slightly edged back, flatter as if it’s missing tissue. Looking from the front its very easy to spot varying degrees of stenotic nares as they appear pinched. Staffords with elongated soft palate can be heard struggling to breathe, even in indoor cooler conditions. I have heard judges comment on how adorable that Stafford smile is when the dog in question is simply struggling to breathe. The smile they are so well known for shouldn’t be coupled with raspy breathing noises. That ‘cute’ snore you love could be a sign of this issue.
As mentioned above, there does exist corrective surgery for BAS and while certainly beneficial to the dogs health, is against AKC show policies and any dog known to have undergone any type of corrective surgery is to be banished from entering any conformation events. That being said, it is commonly performed despite being against AKC policy. Sometimes it is visible and can be detected, other times not so much. As a breed, Staffords worldwide are considered to be ‘at risk’ for this condition and awareness is just starting to spread. We, as preservationist breeders need to be more aware of this and possibly not breed from those affected if possible – or – look for a mating partner with wide open nostrils and a family history of same.
At any rate, more caution should be taken when exercising, especially on humid days. Keeping the affected Stafford in fit condition, not overweight (important regardless of nares status), and building up exercise tolerances are recommended. Keep plenty of cool water, cold coat, spray bottles and fans handy on those hotter days. Do not allow the dog to overheat and keeping them nice and trim should help. We see this in every shape, color and sized Stafford.
Since we know several different corrective surgeries are being performed, as a judge one would need to be able to show proof of an obviously corrected entry to excuse a dog from your ring. In other words, it’s simply not done. The only way you could prove this change has been made is if you judged the dog prior to, and post surgical procedure. Even then, you would need visual indisputable proof. The rules of no altering are in place of course for the health benefits of future generations hoping to discourage breeding of such affected animals. Say for instance, a dog is being campaigned and makes his way to be one of the top dogs in a breed. It is seen by many breeders who could be attracted, take notice and use this dog at stud therefore possibly passing down this deformity which affects the health of future generations. See photo below to visualize stenotic nares. Additionally, if the only examples being shown have stenotic nares and this is all judges and observers see, it quickly becomes the norm.
The corrective surgeries available for this condition are explained below:



Wedge Resection
In typical brachycephalic dog breeds, the veterinarian removes a wedge from the lateral aspect of the alar fold with a #11 surgical blade. This approach differs from other techniques, which remove a wedge of rostral alar cartilage, leaving only a small amount of tissue rostrally on the nares. By performing the lateral wedge, more of the rostral alar fold is spared, allowing a larger, deeper incision and easier suturing.
Laser Ablation
When performing laser ablation, the medioventral aspect of the dorsolateral nasal cartilage is removed . Set the laser at 4 to 5 watts (W) on the continuous cutting setting for best results. Angle the laser in a medial to lateral direction, which keeps the laser from affecting tissue outside the nostril, preventing visible depigmentation.
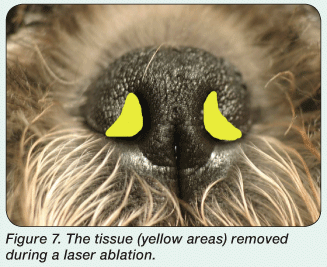
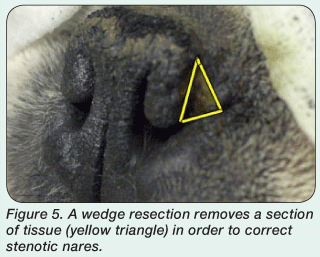
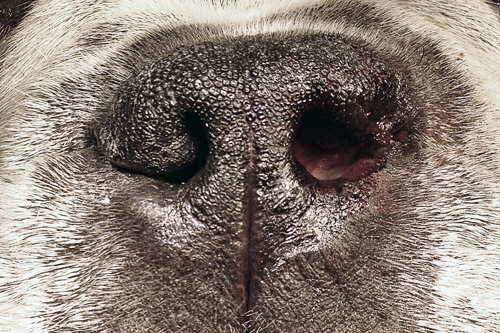
Corrective surgeries are still performed on show dogs despite the rules against this. Its quite common actually. Once you see it, its difficult to miss. Look at nares and study the shapes of the openings. Listen to the dogs breathing. If considering using this stud, ask to see relatives and progeny.
As with most policies, they are in place to give the appearance AKC cares about the health of each breed. And they do, but despite these policies, people correct bites, tails, ears, nares etc anyway. So start paying attention. You might be surprised.
References
Aron DN, Crowe DT. – Upper airway obstruction: General principles and selected conditions in the dog and cat. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 1985; 15(5):891-916.
Wykes PM. – Brachycephalic airway obstructive syndrome. Probl Vet Med 1991; 3(2):188-197.
Koch DA, Arnold S, Hubler M, Montavon PM. – Brachycephalic syndrome in dogs. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet 2003; 25(1):48-55.
Evans HE, de Lahunta A. – Miller’s Guide to the Dissection of the Dog. Philadelphia: WB Sanders, 1996.
Pink JJ, Doyle RS, Hughes JM, et al. – Laryngeal collapse in seven brachycephalic puppies. J Small Anim Pract 2006; 47(3):131-135.
Seim HB. – Brachycephalic syndrome. Proc Atlantic Coast Vet Conf, 2001.
Brdecka D, Rawlings C, Howerth E, et al. – A histopathological comparison of two techniques for soft palate resection in normal dogs. JAAHA 2007; 43:39-44.
Hobson HP. – Brachycephalic syndrome. Semin Vet Med Surg Small Anim 1995; 10(2):109-114.

